food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome fpies adults
The most common FPIES food triggers are cows milk soy rice and oats but any food can cause FPIES symptoms. The list of potential food triggers is varied and can be somewhat region specific.

Foods Commonly Implicated In Food Protein Induced Enteropathy And Their Download Table
The most common triggers are milk and soy but any food even those thought to be hypoallergenic eg.

. The most common triggers include cow milk soy and grains rice barley oats. Lessor reactions can cause extreme nausea and diarrhea. Cows milk soy and cereal grains are the most common trigger foods but other foods have been reported including eggs meats poultry beef pork seafood fish shrimp mollusks peanut potatoes nuts and fruits apple pear banana peach watermelon.
To describe the clinical characteristics prognosis and associated factors in adult FPIES. My Fpies File Cabinet What Is Fpies In 2022 Food Allergies Signs Of Food Allergies Allergies. Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy. Symptoms of FPIES for adults are usually the classic vomiting and diarrhea that occur 2-4 hours after a reaction. In approximately 40 of cases affected individuals may have a reaction to both cows milk and soy.
Solid foods have also been shown to cause FPIES including foods that are generally not considered allergens. Like other food allergies FPIES reactions are triggered by eating a particular food. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to.
Adults with severe reactions can have vomiting to shock just like kids. Rice oat can cause an FPIES reaction. Rice is the most common solid food associated with the disorder.
Objective To describe the clinical characteristics prognosis and associated factors in adult FPIES. FPIES can occur in people of all ages but it most commonly affects children and infants. These symptoms can lead to other complications including changes in blood pressure and body temperature lethargy and failure to thrive.
However little is known about its characteristics. The two most common foods associated with FPIES are cows milk and soy. However little is known about its characteristics.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in adults is being increasingly recognized. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES in adults is being increasingly recognized. Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion Food proteininduced enterocolitis-like syndrome in a population of adolescents and adults caused by seafood.
Unlike typical food allergies FPIES only affects the gastrointestinal GI tract. Patients manifest with symptoms of repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 h of ingesting a food trigger and can also present with pallor and lethargy and diarrhea may present within 510 h. Typical symptoms of FPIES include severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration two hours after eating.
A 10-year prospective study was conducted in the Allergy Section of Alicante General Hospital in adults diagnosed. These symptoms typically show up. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an allergic reaction in the gastrointestinal system.
In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy typically presenting in the first year of life. FPIES typically starts within the first year of life.
It can cause severe vomiting diarrhea and stomach cramping. Egg provoked food proteininduced enterocolitislike syndrome in an adult Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can occur in adults. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
Adults and children have different experiences with food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome although more research is necessary according to a study published in The Journal of Allergy and. They can also have shaking low body temperature or fever.
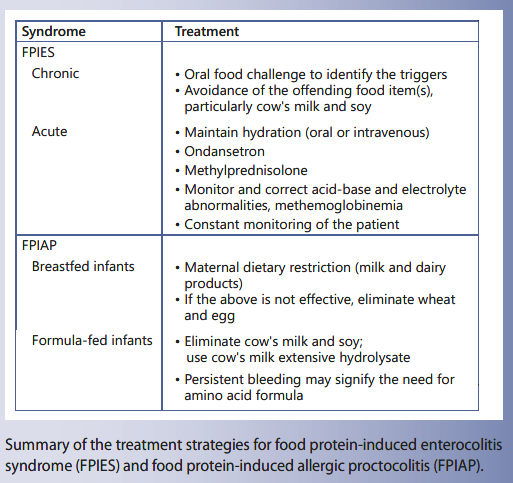
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Classification Scheme Of Fpies Fpies Food Protein Induced Download Scientific Diagram

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Advances In Understanding Immune Mechanisms Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Manifestations Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Scientific Diagram

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Sciencedirect
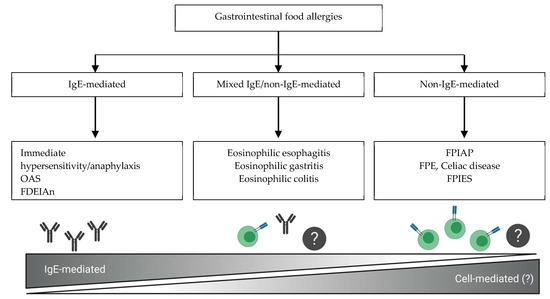
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
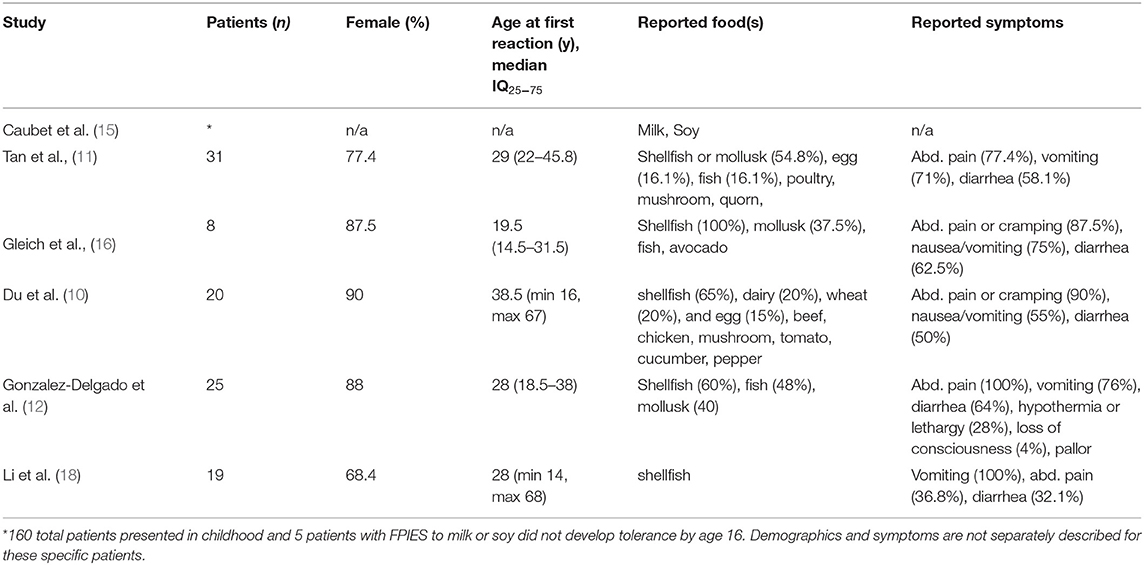
Frontiers Adult Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology